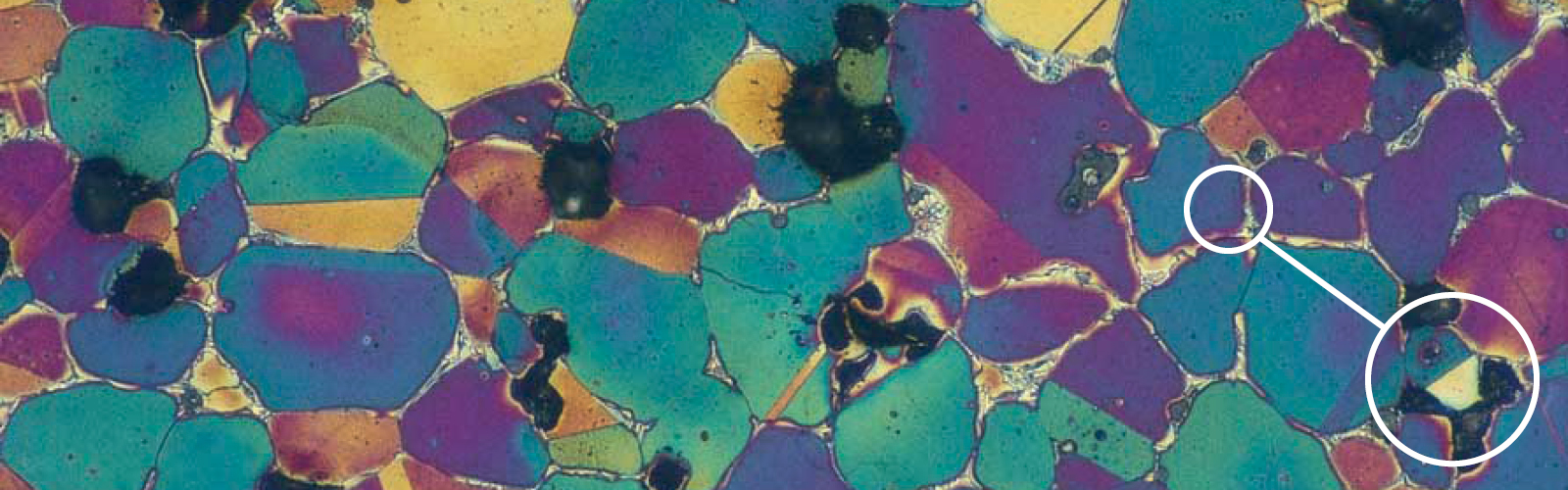
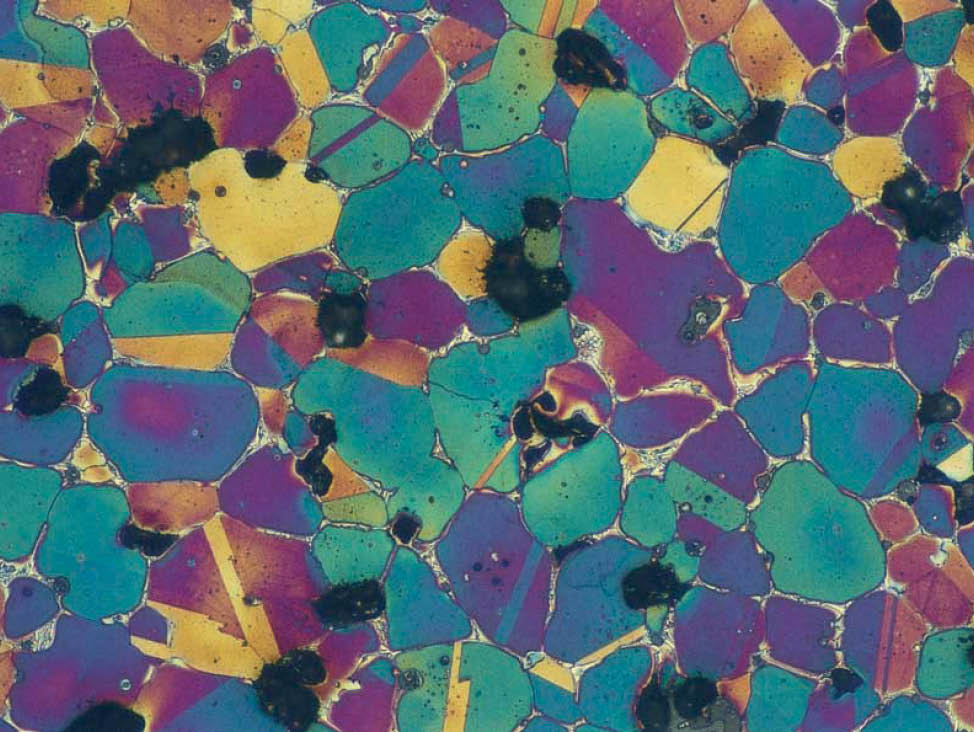
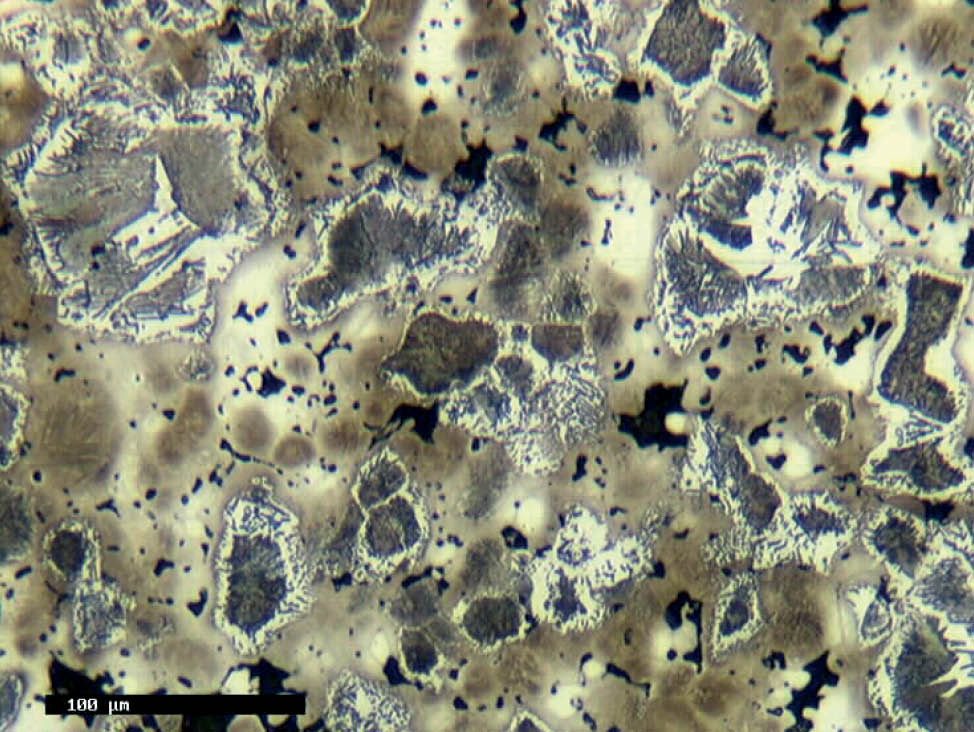
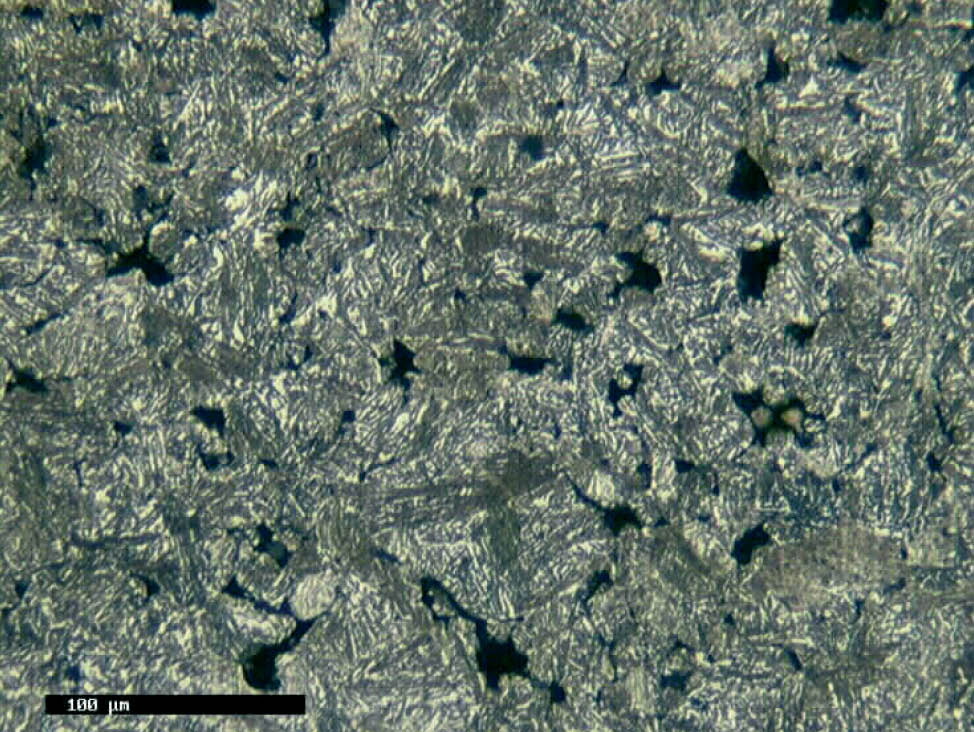
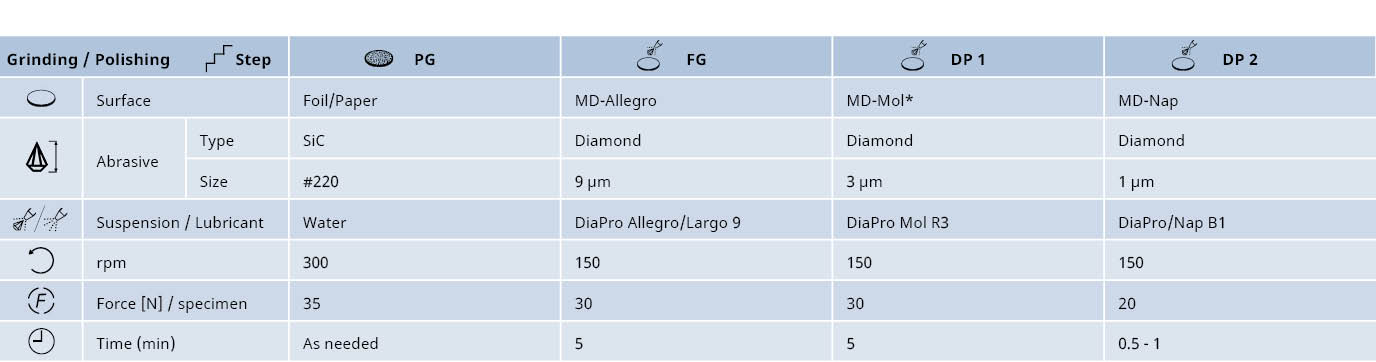
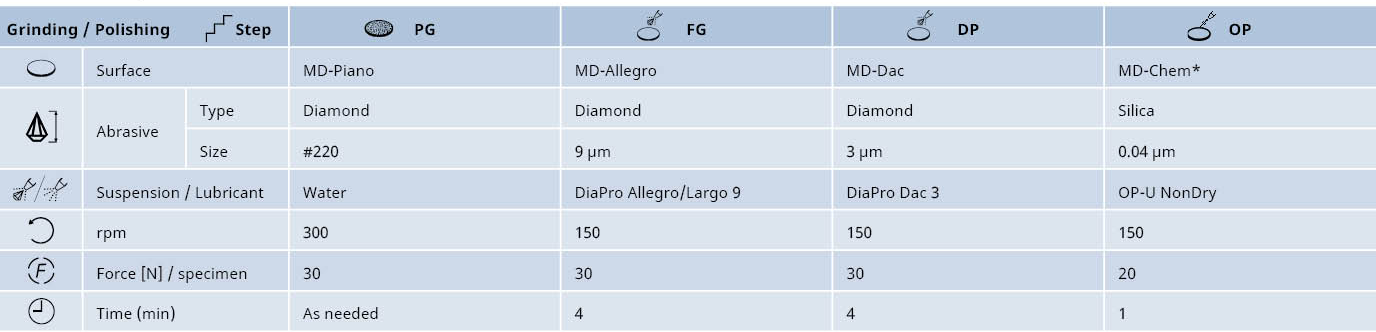
The production of powder metallurgy parts
Many different metals are used to create powder metallurgy components, including iron, copper and steel powders.
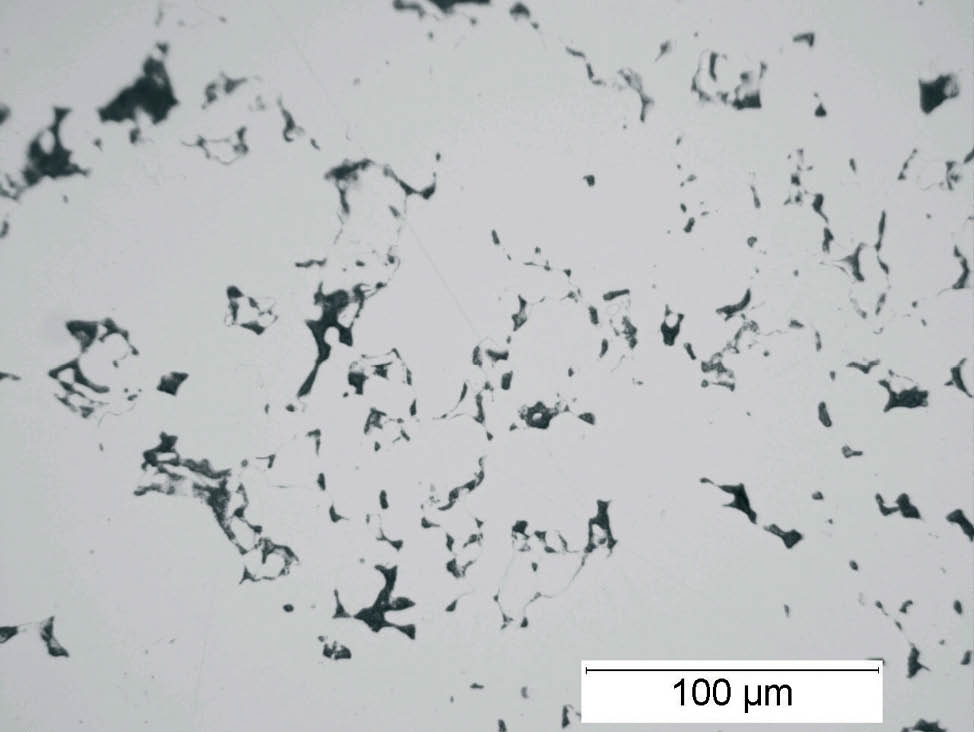
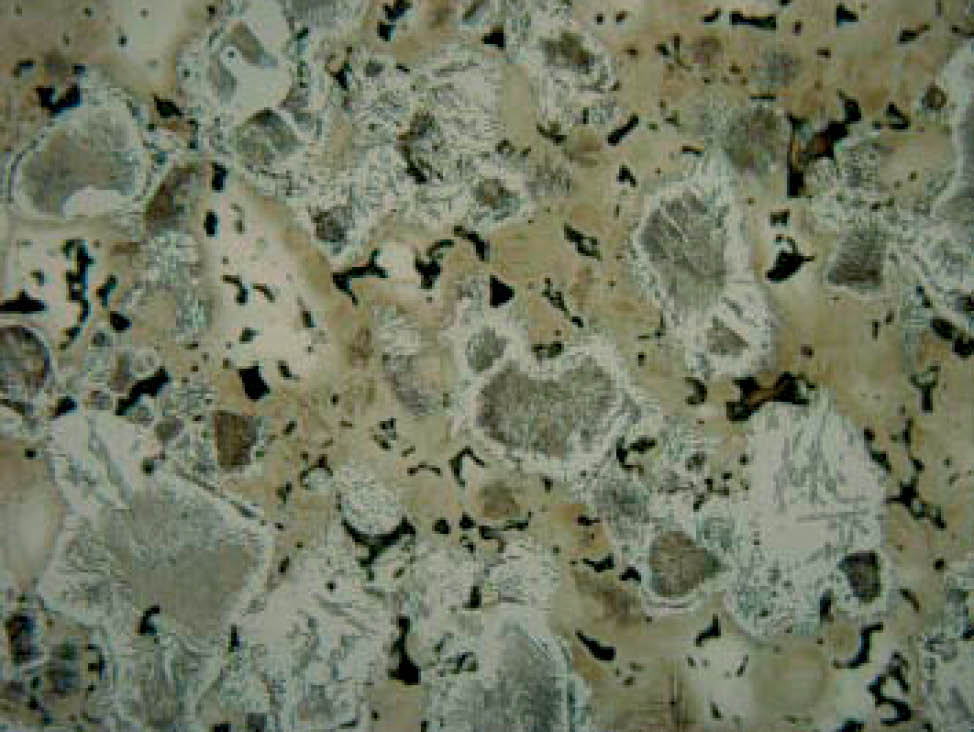
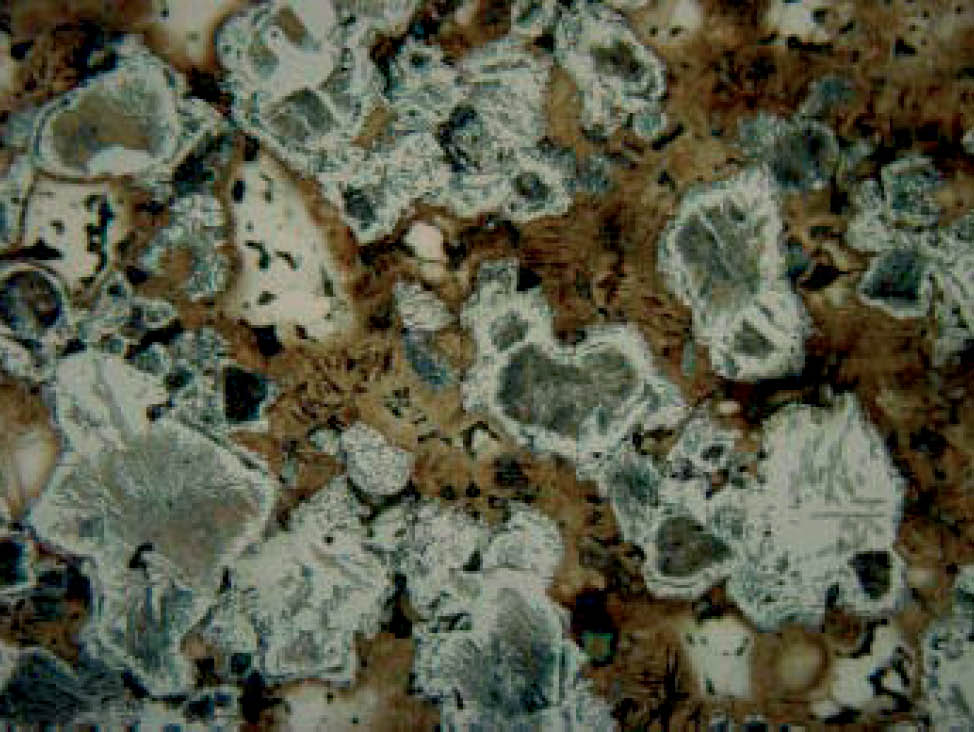
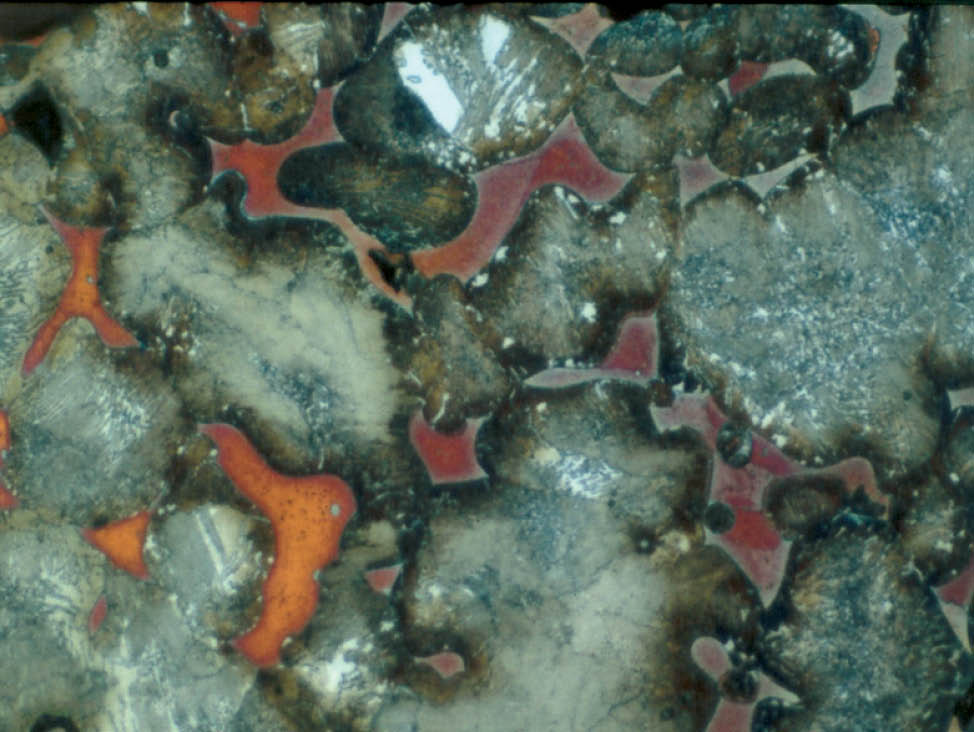
Manufacturing process of iron and steel powders
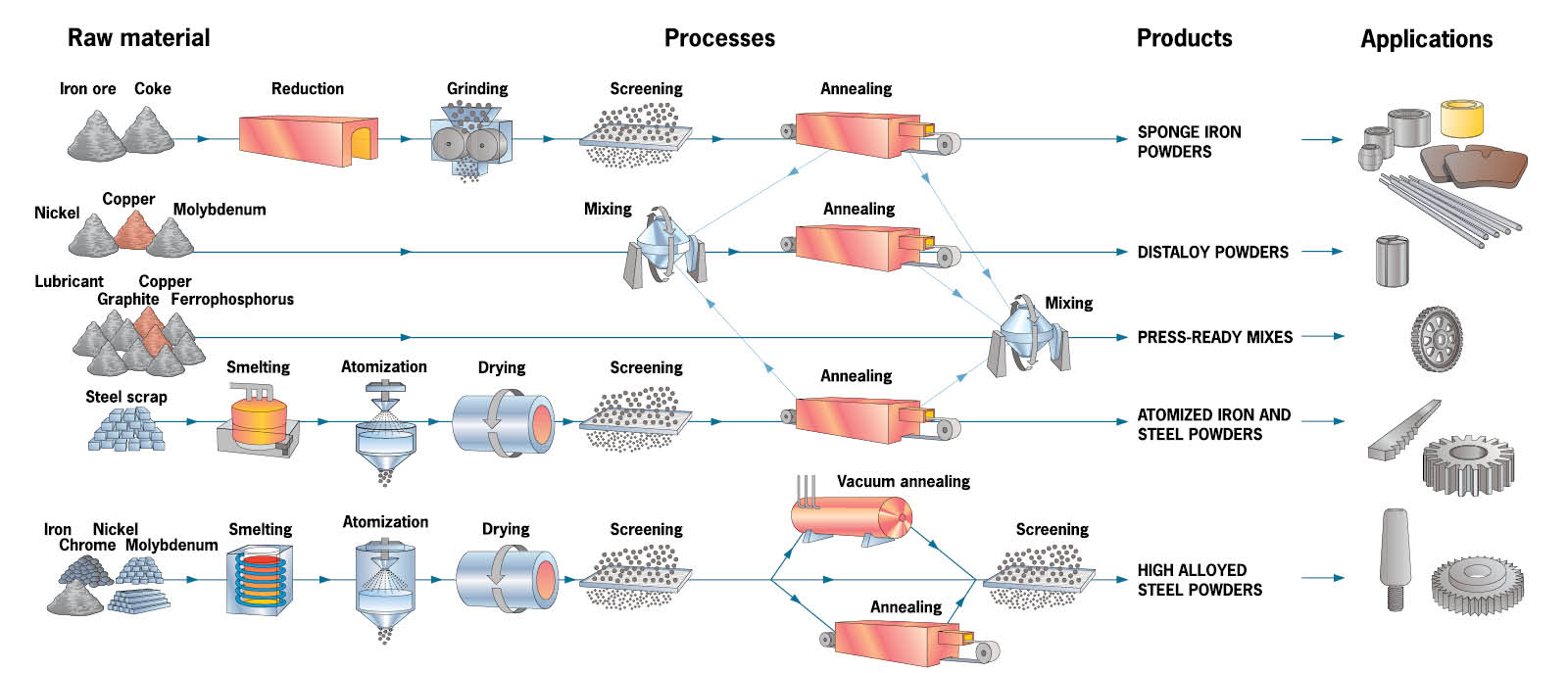 Powder production
Powder production
There are two common methods of powder production: chemical and atomization.
- Chemical: The metal is converted from ore oxides directly to metal powder at a temperature below the melting point.
- Atomization: The molten metal alloy flows through a nozzle and is struck by high-pressure water or gas jet. Small droplets are formed which solidify into particles.
Once produced, the metal powder is mixed. At this stage, other elements can be added, including lubricant, carbon and/or alloying elements.
Compacting the powder in a carbide die
In order to produce components, the mixed powders are compacted under high pressure in a carbide die. At this stage, the part is shaped like the finished component, but does not have the required strength. These components are known as ‘green’ parts.
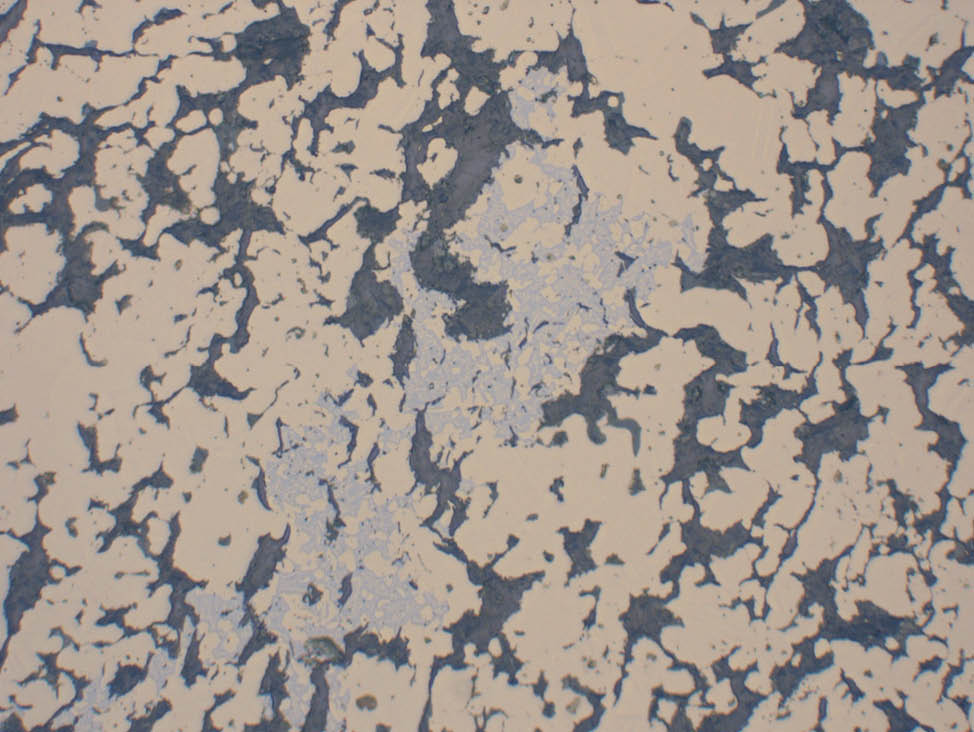
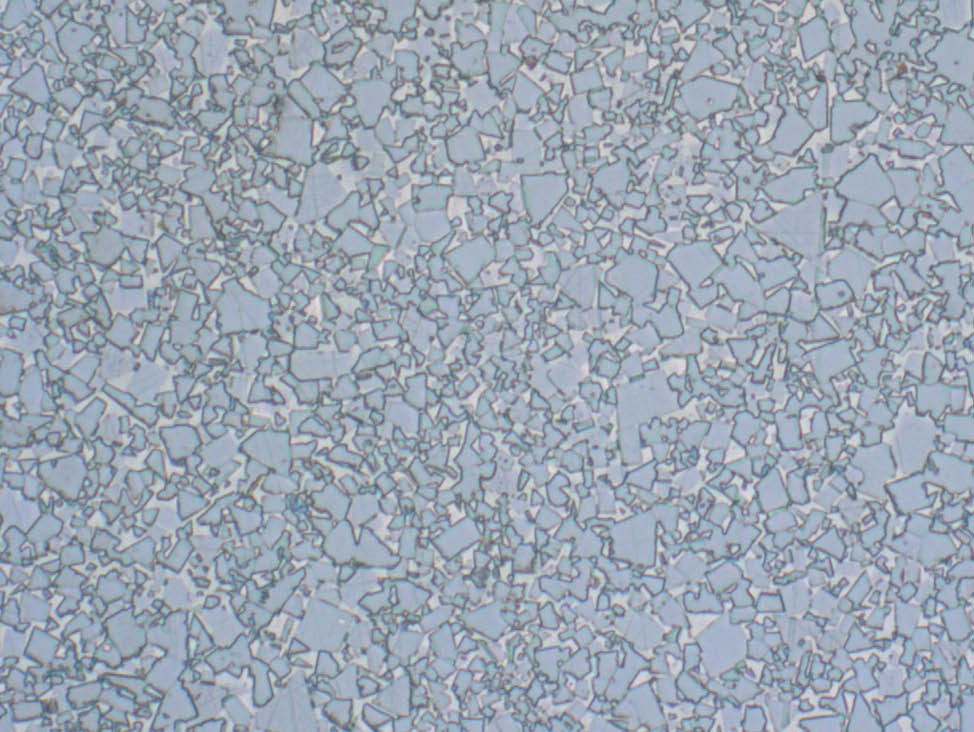
Sintering the component
To develop the necessary mechanical and physical properties, the component is sintered at high temperature in a protective atmosphere. Bonding occurs through diffusion between adjacent particles.
Final treatments
Depending on the application, some parts may undergo additional treatments, including hot isostatic pressing, oil impregnation, surface hardening or plating.
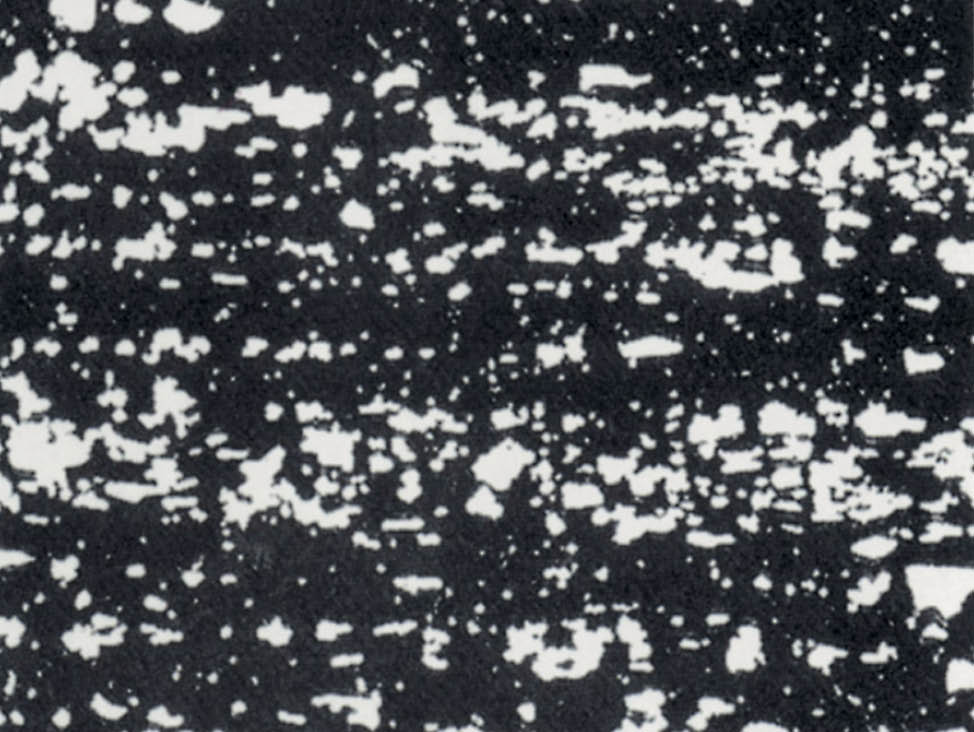
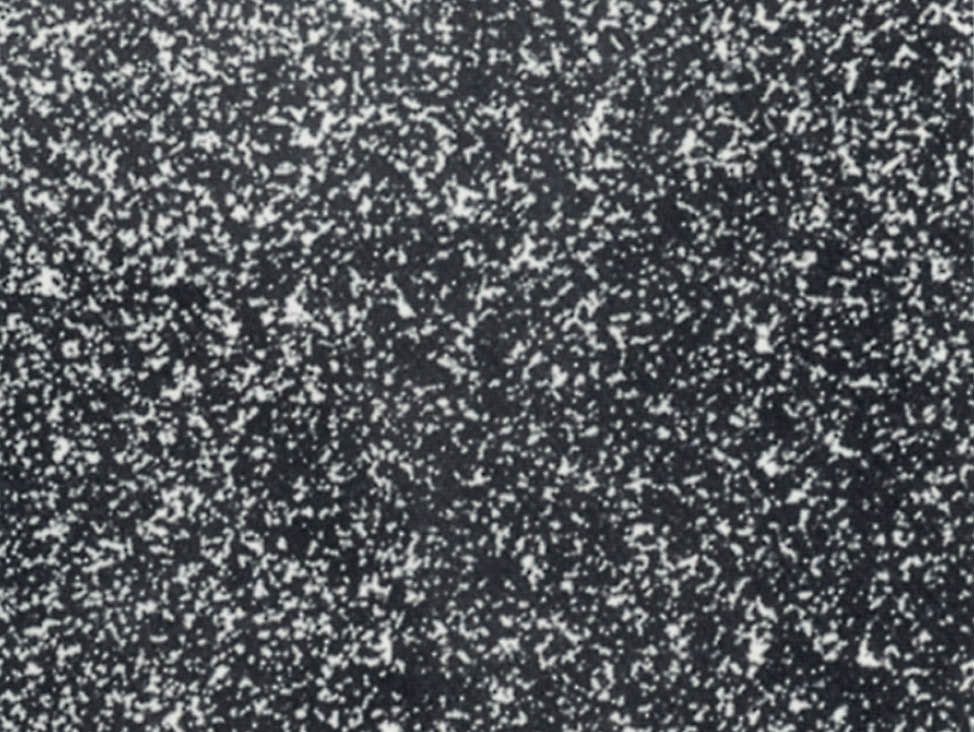
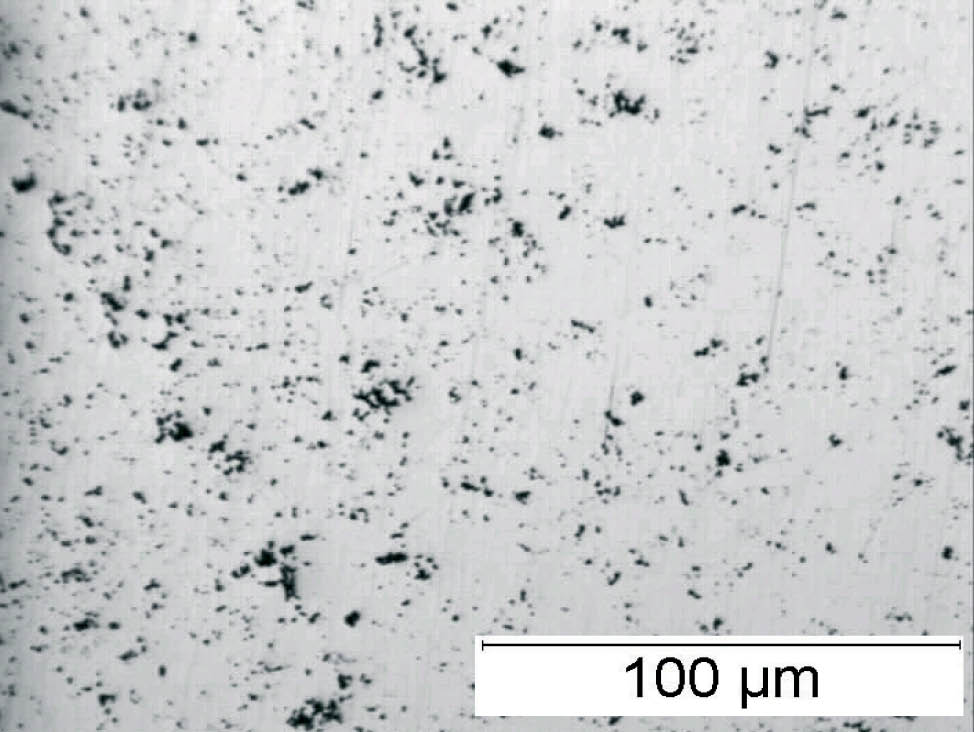
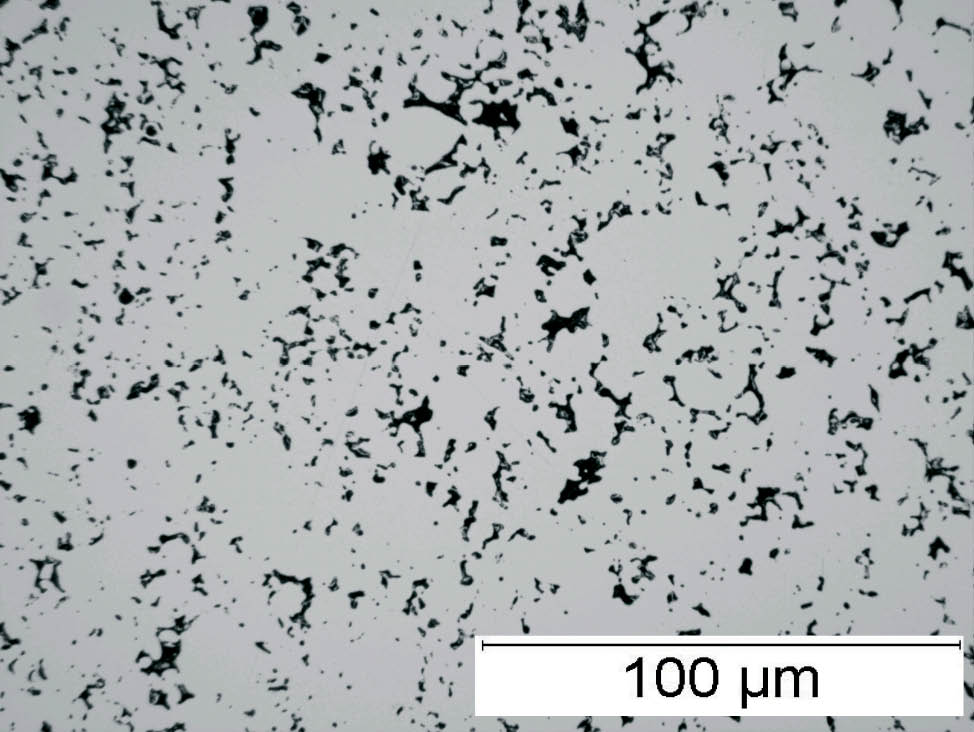
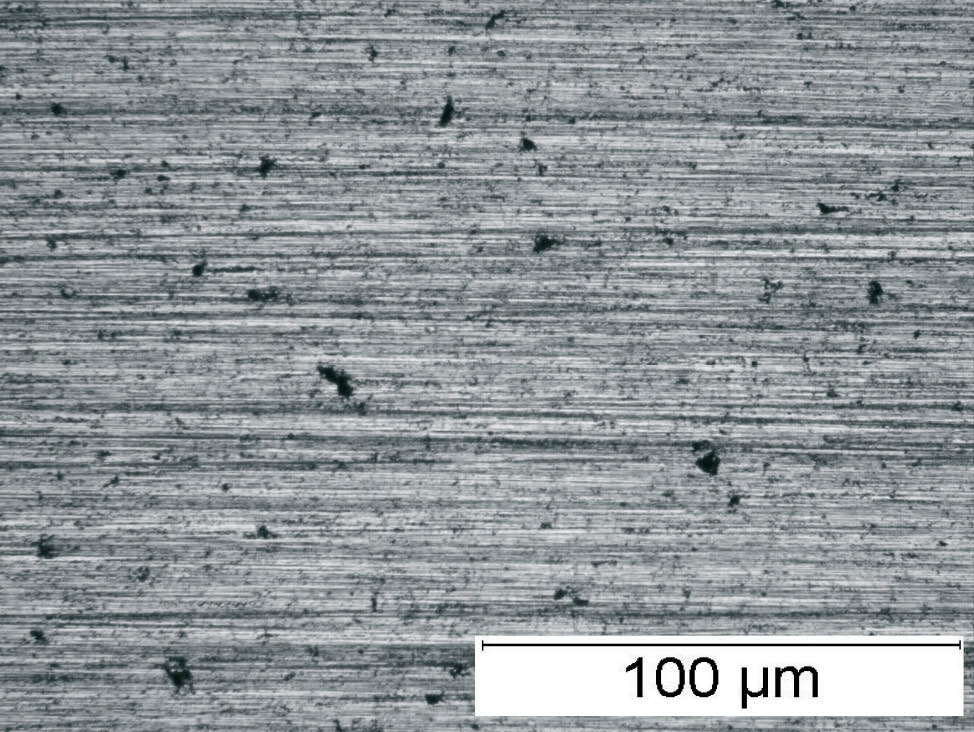
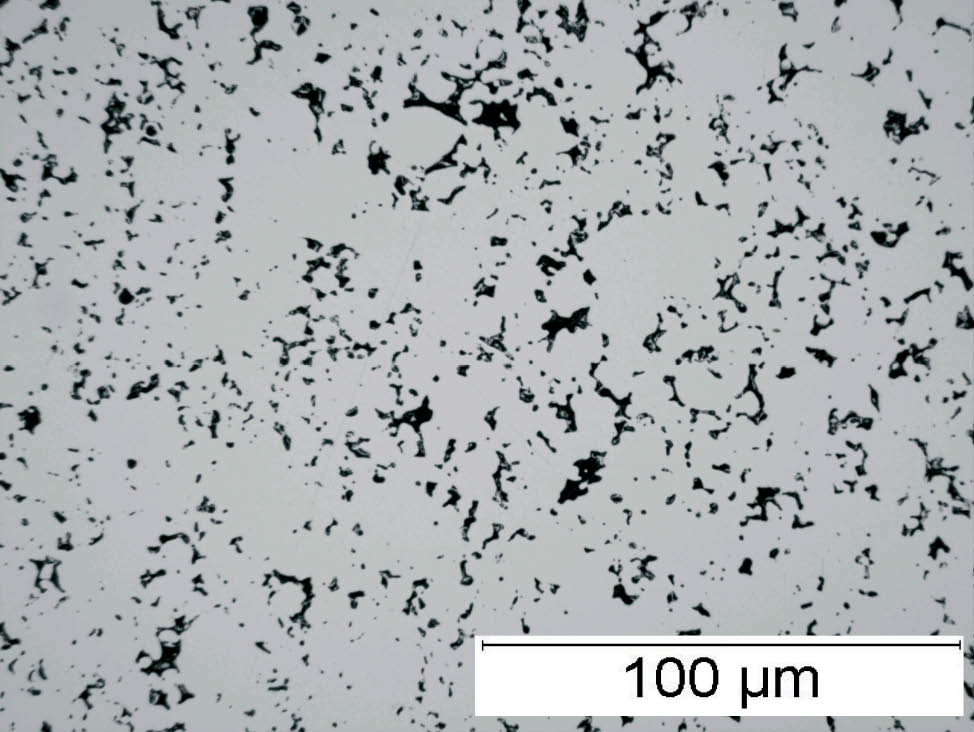
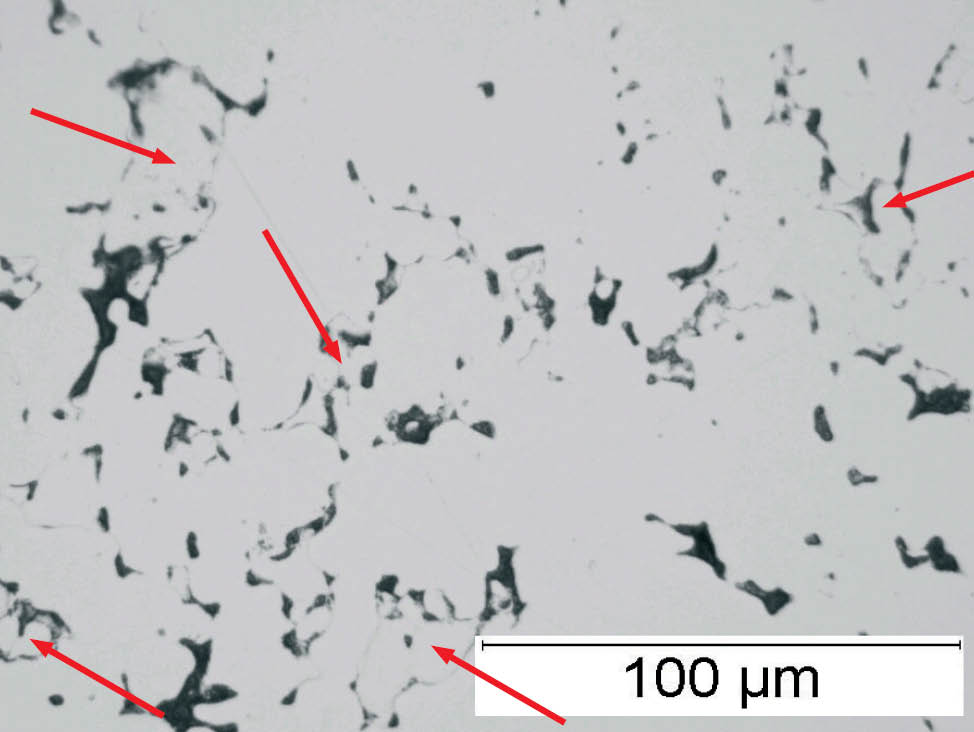
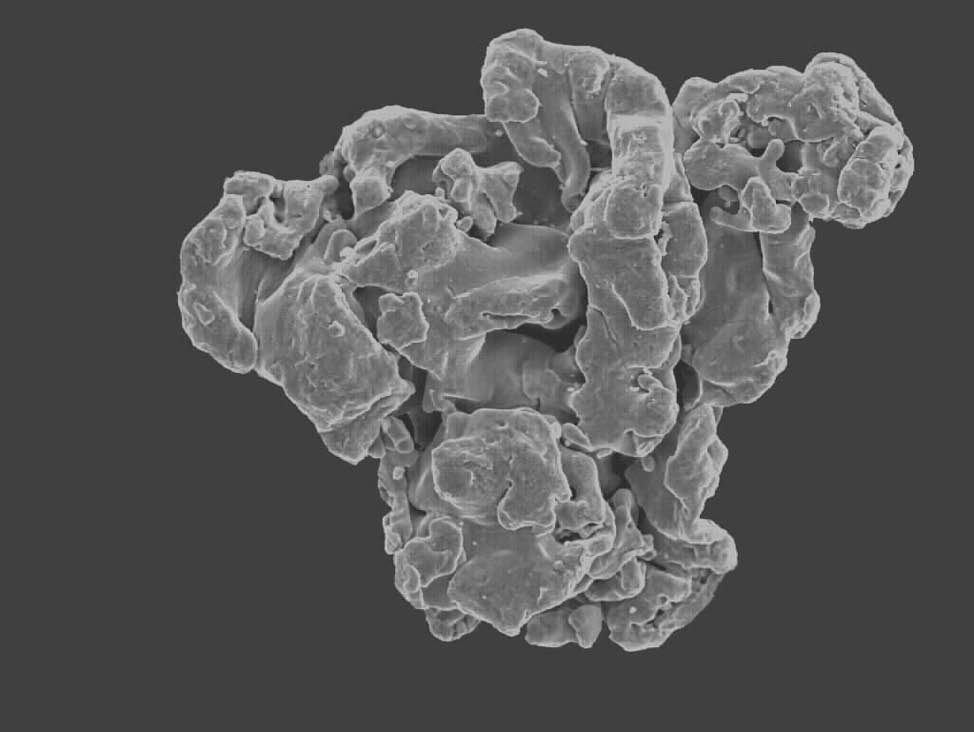 Fig. 4: Sponge iron powder, SEM
Fig. 4: Sponge iron powder, SEM